
24/01/2025
Beneficiation of ore and physico-chemical transformation of concentrates
Within the beneficiation process, the research group at TUD developed an opto-magnetically induced sorting technology. Within the next months, their work will continue developing their code to optimise the colour identification of target metals, and simultaneously on various set-ups to improve the magnetic attraction and and to ensure the seamless integration of all components of their opto-magnetically induced sorter.
Within the same work package, researchers at NTUA have developed a new calcination technology with additives, tested on spodumene concentrates. Using different settings and parameters, such as the processing temperature, reaction time, pressure, the extraction yields for Li ranged between 71 % and 96 %. Depending on the additive type, adjusting the calcination parameters accordingly can significantly reduce impurities, such as aluminum (Al), present in spodumene concentrate. Simultaneously, NTUA partners have been optimising a new technology for Li extraction with calcination from lithic mica and the results will be available in the upcoming communications.
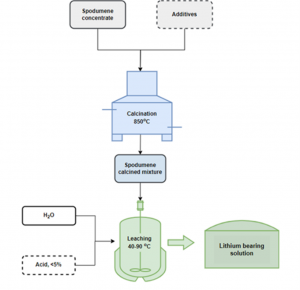
Calcination scheme NTUA
Working on spodumene concentrates, the research group at TEC has established a novel pre-treatment process that allows a relevant improvement in the next leaching process of lithium for its valorisation. As a result of this method, which includes ball milling combined with additive, the transformation of the mineralogical structure of the spodumene takes place at a significantly reduced temperature, ranging from 1100ºC to 900ºC. Based on these findings, TEC has applied a similar approach for the lithium phosphate and the lithic mica materials, reporting good results.
© visual:Adobe Stock Photos